The state of human health can be easily assessed by inspecting the body. The most information can be obtained by observing the hair, skin and nails. Their condition will say a lot about the well-being of your cells. Brittle nails and dull hair often indicate health problems, which need to be detected and cured. Vitamin B has a positive effect for many processes in the human body. The group of these vitamins also includes biotin and vitamin H, which perform important functions for the human body.
Characteristics of biotin
Biotin belongs to the group of vitamin B and is also called vitamin H. The name vitamin H comes from the German word “Haut”, which means skin. The substance is stored in the liver and acts as a carbon dioxide transporter in various processes, which take place in the body. It strongly affects the functioning of the skin and hair. Biotin is very important for the functioning of cells in the whole body. In dry form, it is quite stable, while in acid solutions it loses its biological activity.
This means that it is very unstable and sensitive to temperature changes, heat, UV rays and prolonged contact with water, alkaline compounds and oxygen. It comes in the form of a crystalline, and as a white powder when dissolved in alcohol or water. It also contains sulfur, which performs important functions for the body as well.
Biotin and healthy skin, hair and nails
Biotin is involved in the synthesis of proteins, fatty acids and sugars. It has a huge impact on the proper functioning of the skin, hair and nails. The substance is recommended for people with brittle hair, weak nails and dry skin. Vitamin H is great for treating adolescent acne, because it prevents the increased activity of sebaceous glands. It takes about three to four months of regular biotin supplementation to improve the condition of your nails.
Biotin and the nerve system
Vitamin interacts with amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine), which are active substances in the muscles. This is crucial for providing energy to the nerve system. Therefore, high levels of biotin have an impact on well-being, pain, sensory sensitivity and vitality.
The effect of biotin on glucose, muscle and joint function
Studies have shown, that biotin stimulates the metabolism of hepatic glucose. It stabilizes the glucose level in your blood. Biotin is therefore extremely important for people with diabetes. Biotin actively cooperates with ingredients responsible for the proper functioning of muscles and joints. Its deficiencies may cause neurological symptoms, e.g. hand and muscle tremor, or arthritis.
How to use biotin?
When taking biotin, there are a few rules you have to remember. The absorption of biotin is prevented by avidin, an alkaline glycoprotein found in the egg of a chicken. You should therefore avoid eating raw eggs. Also, alcohol can cause a reduced absorption. Biotin is excreted in breast milk. Therefore, do not use biotin supplements on your own, during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The effects of a biotin deficiency
Vitamin H deficiencies are extremely rare in adulthood. The reason for the deficiency includes a long-term antibiotic treatment, which can reduce the amount of biotin. In case of a biotin deficiency, the first signal will be dry or flaky skin, hair loss and brittle nails. You may also feel weak and be frequently tired. The deficiency can also cause depression, apathy, drowsiness, hallucinations and increased nervousness.
Experts say, that biotin deficiencies can cause liver enlargement and high cholesterol. Deficiencies can also cause cradle cap or seborrheic dermatitis for infants. For young children, biotin supplementation requires consent from the doctor.
What are the main sources of biotin?
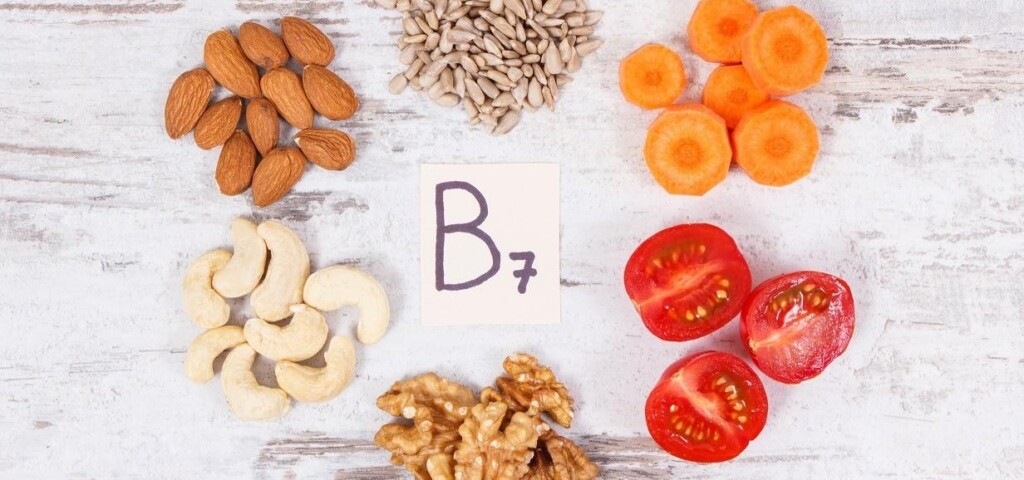
Biotin is found in small amounts in all animal and plant cells. In food products, it is presented in the bound form as biotin esters, or amides. The daily requirement for biotin is 0.02 mg. As you can see it is quite low.
Products rich in biotin for example are cooked yolk, cheese, butter, sea fish, brewer’s yeast, liver, nuts, milk, lentils, cauliflower and cereal grains. Biotin is formed in the large intestine, but its absorption is very low. Although pharmacies sell products, that contain 5 mg of biotin, there are also supplements being sold, that contain only 1 mg of the substance. And what is even worse, they often also contain additives, such as silicon, zinc or a group of B vitamins.