Seborrhoeic dermatitis, also known as seborrhoea, is a chronic and recurrent disease. The symptoms on the skin are unsightly and can result in discomfort or low self-esteem. Normally, the disease affects teenagers during puberty but in some cases adults and babies experience seborrhoeic dermatitis as well.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis – characteristic features
Seborrhoeic dermatitis symptoms include scaly skin on the scalp. They can also occur on the face and other parts of the body. The main cause of seborrhoeic dermatitis is inflammation which results in excessive skin flaking. Mainly young men experience seborrhoeic dermatitis but it can also affect women and people of all ages. The main symptoms include red and scaly skin which is sometimes itchy. The intensity of the symptoms are different depending on the case. In some patients symptoms occur only on the scalp and in others they are situated on the face and chest.
Causes and predispositions to seborrhoeic dermatitis
One of the main causes of seborrhoeic dermatitis is the hyperactivity of sebaceous glands and inappropriate sebum contents. It has also been noticed that patients with a weak immune system is more prone to seborrhoea. Other risk factors include the following diseases: diabetes, AIDS, hepatitis C, Down syndrome and other diseases that weaken the immune system. Patients with epilepsy, facial nerve paralysis and depression are also more prone to seborrhoeic dermatitis. Factors which contribute to seborrhoea include improper skin care, chronic stress, alcohol abuse, eating disorders, irritation caused by chemicals in cosmetics, frequent sunbathing and long-term skin irradiation e.g. using a sun tanning bed.
Dandruff is a milder form of seborrhoeic dermatitis. The cause of dandruff is linked to Malassezia yeasts on the skin. Many doctors say that Malassezia yeasts play an important role in seborrhoeic dermatitis. The higher the yeast count, the more difficult it is to cure it – as it is likely to come back.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis symptoms
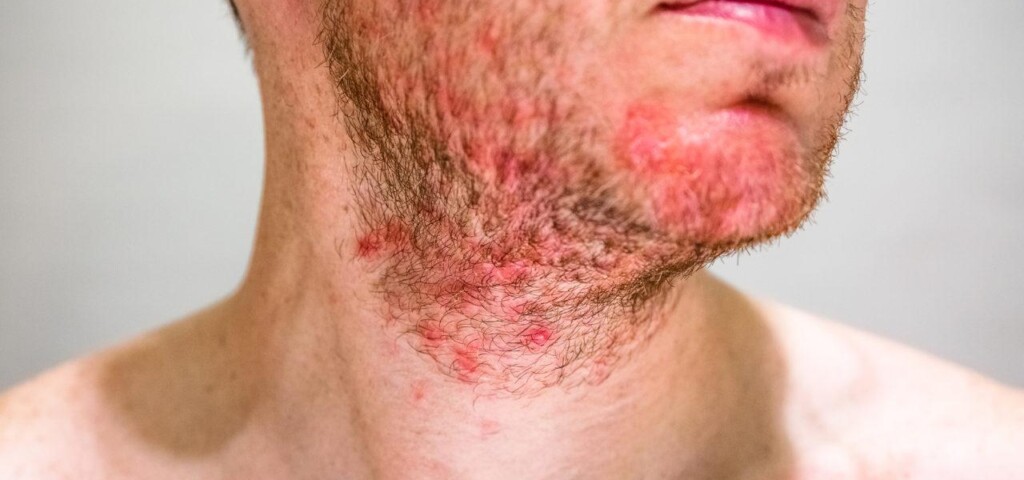
The first symptoms of seborrhoea include excess sebum production on the scalp. The skin is shiny and looks unwashed. In the area of the sebaceous glands there are erythema spots and the skin flakes are yellow due to excess sebum and in some cases there are scabs on the skin. The disease symptoms worsen in autumn and winter when the skin is less exposed to sunlight. At the beginning the lesions occur on the scalp and spread to the face. Some patients experience skin problems along the spine or in the sternal region. The advanced disease stage is characterized by rhagades formed as a result of frequent itching. In the case of acute inflammation there are red exudates particularly in those areas with poor access to oxygen. Parts of the body with many sebaceous glands are the most frequently affected by the disease. They include the eyebrow area, chin, nasolabial folds, mid-forehead, upper lip and sometimes even cheeks.
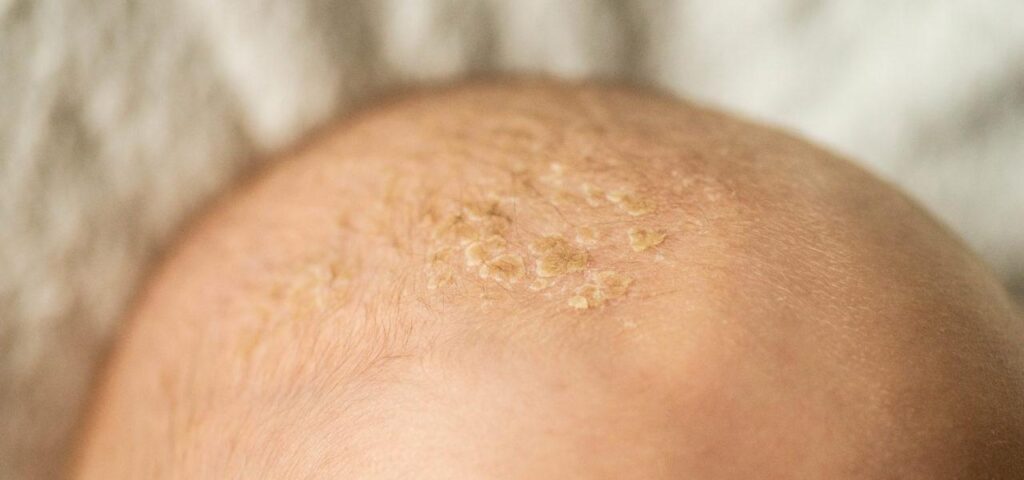
Seborrhoeic dermatitis in babies
Seborrhoeic dermatitis in babies is called cradle cap. It occurs on the scalp as greasy patches of scaling accompanied by scabs. The flakes are usually brown or yellow and they gradually tend to disappear from the skin. In most cases cradle cap is harmless and disappears within a few months. The disease in babies can affect also other parts of the body and diaper area. In most cases cradle cap causes only slight itching. No medication can cure seborrhoeic dermatitis but appropriate treatment allows to reduce the development of the diease. A treatment method suitable for the patient’s needs allows to get rid of flakes from the skin and reduce skin itching and infections.
In most cases it is not required to start treatment but it is worth consulting a doctor who can recommend application of a medication. Cradle cap normally affects 6-12 month old babies and cases of seborrhoeic dermatitis in babies are very rare.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis at puberty and in adults
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is very rare before puberty. Puberty is characterized by intensive hormonal changes and increased activity of the sebaceous glands. High amounts of sebum are produced resulting in shiny skin and infections. Skin intensively responds to irritation and epidermis starts to flake. In addition, sebum contents change and triglycerides level increases during puberty. Over time seborrhoeic dermatitis problems are less frequent but still men are more prone to this disease due to a male sex hormone i.e. testosterone. In some cases the disease can affect people over 50. However, it depends on the individual patient, his/her medical history and previous treatment.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis diagnosis and treatment
If you notice scalp lesions, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist. Usually, it is not required to do additional tests to confirm a diagnosis for the disease. Skin lesions examination and recognizing their character allows making a diagnosis and a recommendation for the appropriate treatment method. In some cases it is recommended to do blood tests and a histopathological examination. Seborrhoeic dermatitis treatment is a real challenge for a doctor. It depends on a few factors such as the patient’s age and the development stage the disease is at. In most cases doctors recommend local treatment i.e. using topical creams with antifungal and anti-inflammatory agents.
At the beginning of the therapy the patient uses a formulation to exfoliate epidermis. Mild shampoos for daily hair care are recommended to wash hair and the scalp. They contain mild ingredients and substances that prevent dermatophytosis. In some cases oral medications are also administered especially in patients with acute skin lesions and who do not respond to current treatment methods. Only adults with the recurrent disease are treated with oral medications such as antibiotics, retinoids and steroids. Disease treatment is really problematic and sometimes takes many years. However, it is worth start treatment to stop the development of the disease.
Prevention
It is recommended to take special care of the skin after treatment. Use shampoos with ciclopiroxolamine or ketoconazole once a month for about 6 months as preventative steps. Use also exfoliating and anti-seborrhoeic body scrubs with salicylic acid and mandelic acid. It is also advised to use creams with anti-fungal ingredients and avoid soap which will make the skin dry and irritated. Other factors intensifying the symptoms of the disease are stress, fatigue and different stimulants so it is recommended to avoid them. You should apply on your face special cosmetics with therapeutic ingredients. A well balanced diet is also a natural way to prevent the disease.
You can rub different essential oils such as eucalyptus oil, mint oil, chamomile oil, lavender oil or almond oil into itchy areas. In beauty salons you can have different treatments but you should consult a dermatologist to see which treatments you can try and how often they can be done. Beauty salons offer mineral masks rich in zinc, sulphur, copper, sericite, calcium, quartz or silicon. They also offer treatments for oily skin (with excessive seborrhea production) e.g. cavitation or iontophoresis. However, it is important to note that appropriate daily skin care is of vital importance.





Panie Doktorze, czy są jakieś zabiegi dostępne w salonie kosmetycznym/w klinice dermatologii estetycznej, które mogłyby wpłynąć na zmniejszenie objawów łojotokowego zapalenia skóry?
Dzień dobry,
Tak są dostępne serdecznie zapraszamy na konsultacje do Pani Doktor Osipowicz. https://katarzynaosipowicz.pl/
Pozdrawiam
Piotr Turkowski