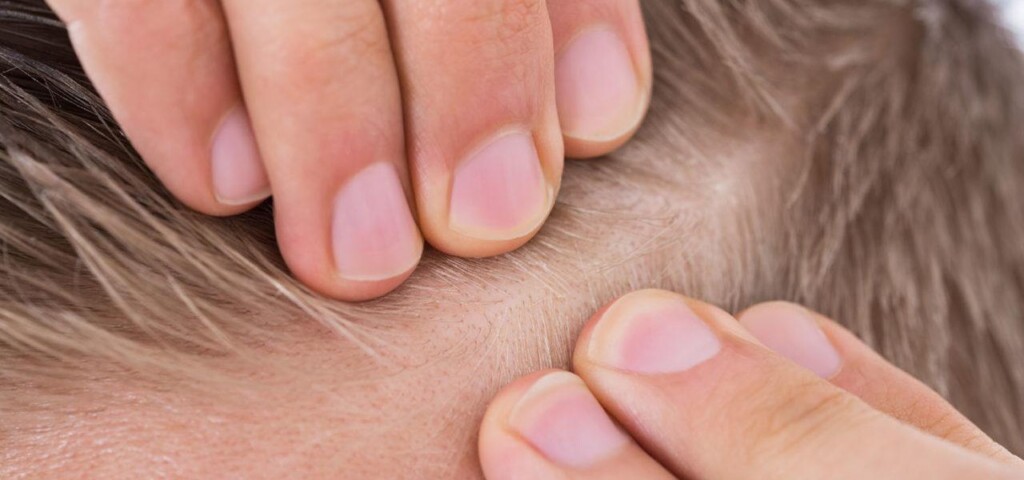
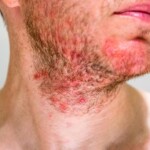
Itchy scalp is not only a very bothersome problem but also a symptom of many conditions. Patients who experience this issue often blame it on improper hair care and treat it as a cosmetic defect. When neglected, however, it can become a serious condition that may lead to temporary or even permanent hair loss! So, what are the causes of scalp itching?
What causes scalp itching?
There are many possible causes of this phenomenon, and almost everyone has experienced this unpleasant condition at least once. Some causes of itchy scalp—such as seborrheic dermatitis—affect the entire scalp, making it greasy. Other conditions—such as contact dermatitis—affect sensitive and dry scalp. There are also other causes of itchy scalp that are not related to skin or hair type—for example, head lice.
- In seborrheic dermatitis, the exact etiology is not fully known. However, it is believed to have an immunological basis and result from dysfunction of the sebaceous glands located next to hair follicles. Symptoms are further aggravated by the presence of Malassezia yeast.
- Itchy scalp can also result from atopic dermatitis—a genetically determined condition. Factors that worsen symptoms include environmental pollution, food allergens, fungi such as Malassezia or Candida albicans, and psychological stress.
- Another cause of scalp itching is fungal infection. Depending on the type, symptoms may include hair loss combined with flaking skin, as well as painful infiltrates or inflammatory nodules filled with pus.
- Psoriasis is another condition that patients with itchy scalp often suspect. It manifests as characteristic skin lesions caused by disrupted epidermal regeneration. They are clearly defined, reddish/brownish in color, and covered with scaling.
- Another cause of itchy scalp is allergic contact dermatitis. This is caused by small-molecule haptens that penetrate the skin and trigger an immune response. For eczema to appear, the patient must have a predisposition to contact allergy. Common triggers include nickel, formaldehyde, and fragrances.
What characterizes dandruff?
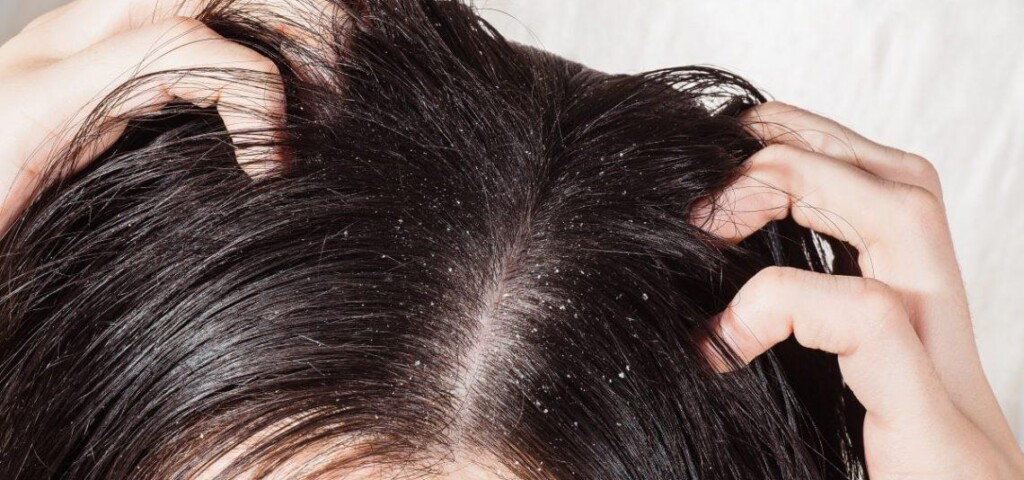
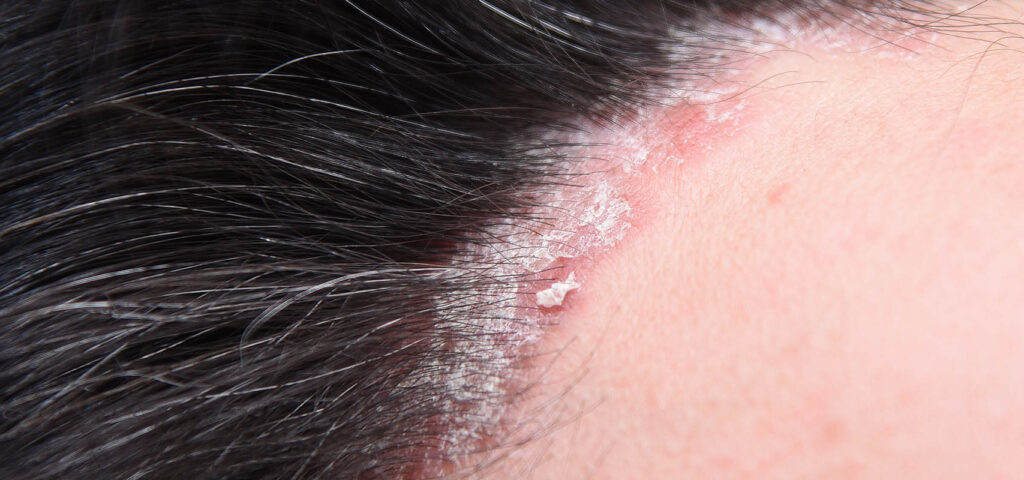
Dandruff is a type of fungal condition caused by Malassezia yeast. This lipophilic species uses lipids in human sebum as an energy source for growth and development. Metabolites produced during triglyceride breakdown irritate the skin, causing inflammation and accelerating the shedding of dead epidermal cells. This leads to the typical flakes and white scales on the scalp, which may take the form of dry or oily dandruff. The condition is recurrent and influenced by genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Treatment usually involves using an anti-dandruff shampoo containing antifungal active ingredients.
Why does seborrheic dermatitis cause itching?
This is an inflammatory condition that affects areas with many sebaceous glands—such as the scalp, chest, or back. As with dandruff, Malassezia yeast, excessive sebum production, and abnormal epidermal cell renewal play a major role in its development, leading to accelerated keratinization. Seborrheic dermatitis often occurs alongside oily dandruff, and has a recurrent and chronic course.
Read more: Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp – causes, treatment
This condition often appears during adolescence when sebaceous glands are overactive. Another peak occurs after the age of 50. Symptoms include red skin, flaking, and itching that worsens with stress and sweating. Treatment also involves antifungal shampoos and medications.
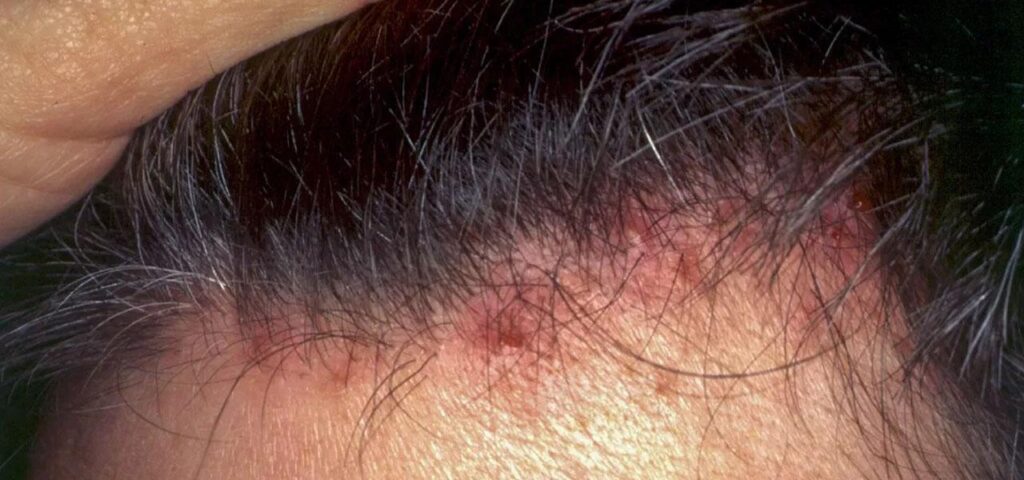
What is the course of psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease of autoimmune origin. Malassezia fungi can worsen skin condition, and the disease is linked to immune system dysfunction. A normal skin cell cycle lasts 28 days, during which cells form, mature, die, and shed. In psoriasis, the immune system signals prematurely, shortening the process to just 3–4 days. New cells mature quickly while old ones fail to shed, forming thick layers of dead skin called scales. Symptoms include red, scaly, itchy patches covered with silvery flakes. Scraping the scales causes them to flake off, revealing a shiny surface.
Read more: Scalp psoriasis – causes, symptoms, treatment
Treatment usually involves topical therapy that removes excess scales and slows down cell overproduction. Moisturizing and oiling the scalp are also important to prevent micro-damage.
What is atopic dermatitis?
This is a chronic, recurrent inflammatory condition of the scalp with an allergic background. It is characterized by intense itching and typical localized skin lesions. It usually occurs in children but can also develop in adults. The disease may last a lifetime, but in most cases, symptoms improve by school age.
Atopy is the inherited tendency to overproduce immunoglobulin E and develop immediate allergic reactions to minimal allergen exposure. Malassezia fungi play a key role in AD development. Lipid metabolism in the epidermis is impaired, weakening the hydrolipid barrier. Additionally, intercellular “glue” fails to bind cells tightly, making the skin permeable to irritants and allergens. As a result, atopic skin is dry, rough, and itchy. Symptoms may include redness, small pimples, bumps, and even thickened scales.
Severe cases are treated with anti-inflammatory and antifungal drugs. Proper care is also crucial, including shampoos with moisturizing ingredients.
Patients with AD often fall into a vicious cycle: dryness and itching cause scratching, which further damages the skin, increases dryness, and facilitates allergen penetration. This worsens local inflammation and intensifies itching.
What is contact allergy of the scalp?
This is an acquired hypersensitivity to a specific allergenic substance. It occurs when the scalp comes into contact with the allergen, causing itching, eczema, and redness. Common allergens include:
- Nickel – found in hair accessories,
- Paraphenylenediamine – a hair dye ingredient,
- Propylene glycol – a solvent in cosmetic sprays,
- Sodium lauryl sulfate – a shampoo ingredient,
- Formaldehyde – used in hair-straightening treatments,
- Cocamidopropyl betaine – a detergent used in shampoos,
- Fragrance substances.
If contact allergy is suspected, the allergen must be eliminated immediately. Treatment involves topical soothing medications prescribed by a dermatologist or trichologist.
What characterizes a dry scalp?
Scalp itching is also a symptom of dryness that occurs without visible flaking. The problem usually results from improper hair care, external factors, or hormonal changes. It can also be caused by conditions affecting skin structure and function or systemic diseases. Quick improvement can be achieved with dermocosmetic shampoos. Additional treatment support may include mesotherapy in an aesthetic medicine clinic.
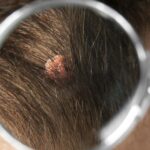
What is folliculitis?
A hair follicle is a small pocket in the skin from which a hair grows (learn about hair structure here). Each follicle has its own sebaceous gland that produces sebum to moisturize the scalp. At the base of the follicle is the papilla, surrounded by a matrix of hair cells. These cells grow and mature to emerge as new hair. Sometimes, inflammation develops in the follicle due to bacteria (such as streptococcus or staphylococcus). This results in pustules, redness, and itching. Depending on the pathogen, treatment involves different antibiotics or antifungal medications prescribed by a dermatologist.
Read more: Folliculitis – causes, symptoms, treatment
Does head lice cause itching?
Yes, head lice are a contagious condition caused by *Pediculus humanus capitis*. They inhabit the scalp and lay eggs in the hair. Lice feed on blood, and the bite causes inflammation with intense itching. The most obvious symptom is frequent scratching. Treatment is topical and involves shampoos or sprays with anti-lice agents.
What else causes scalp itching?
Few realize that vitamin deficiencies significantly contribute to scalp itching. A lack of essential nutrients can affect both hair and scalp health. Itching is closely linked to B vitamins.
Stress also negatively impacts scalp condition. Strong emotions can manifest as itching. Numerous studies show that stress-related hormonal imbalances are linked to scalp itching. Cortisol, adrenaline, and noradrenaline, which regulate emotions, may also cause dry mouth and an irresistible urge to scratch the scalp.
How to treat an itchy scalp?
Treatment depends on the type and cause of the condition. Topical methods include medicated shampoos or creams. In severe or recurrent cases, oral therapy is combined with topical treatment.
Proper scalp hygiene is essential—especially frequent washing with hypoallergenic shampoos. Patients should choose products formulated for dry and sensitive skin. Home remedies can also help:
- Menthol for its anesthetic and soothing effect,
- Camphor for a cooling sensation,
- Cold compresses using frozen items,
- Plantain infusions, which naturally relieve itching.
Regardless of the cause, when the first symptoms appear, it is best to consult a dermatologist or trichologist. Based on a scalp examination, patient history, and dermatoscopy, the specialist can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend tailored treatment.