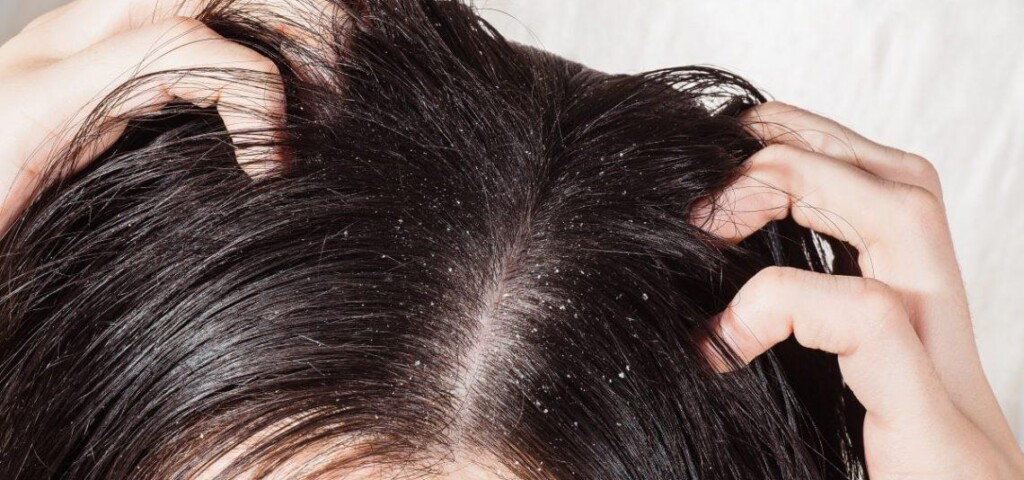
Itching of the scalp is not only a very persistent problem, but also a symptom of many diseases. Patients with this problem very often blame it on inadequate care and treat it as a cosmetic defect. Underestimated additionally, it becomes a more serious phenomenon that can lead to temporary or even permanent loss of hair on the head! So what are the causes of itchy scalp?
- 1. What causes an itchy scalp?
- 2. What are the characteristics of dandruff?
- 3. Why does seborrheic dermatitis cause itching?
- 4. What is the course of psoriasis?
- 5. What is atopic dermatitis?
- 6. What is scalp contact allergy?
- 7. What are the characteristics of a dry scalp?
- 8. What is folliculitis?
- 9. Does head lice cause itching?
- 10. What else causes itchy scalp?
- 11. How to treat an itchy scalp?
What causes an itchy scalp?
There are many reasons for this phenomenon, and surely everyone has experienced this unpleasant condition at least once. Some causes of scalp itching – seborrheic dermatitis – also affect the entire skin, which becomes oily. Other conditions – such as contact dermatitis, affect a sensitive and dry scalp. There are also other causes of itchy scalp that are not dependent on skin and hair type – such as head lice.
- In the case of seborrheic dermatitis, the etiology of the condition is not fully known. However, it is believed to have an immune basis and is due to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, which are located next to the hair follicles. Symptoms are further exacerbated by the presence of yeasts of the genus Malassezia.
- Atopic dermatitis, a genetically determined disease, can also be the underlying cause of an itchy scalp. Factors that exacerbate symptoms include. Environmental pollution, food allergen, Malassezia fungi or Candida albicans or psychological factors.
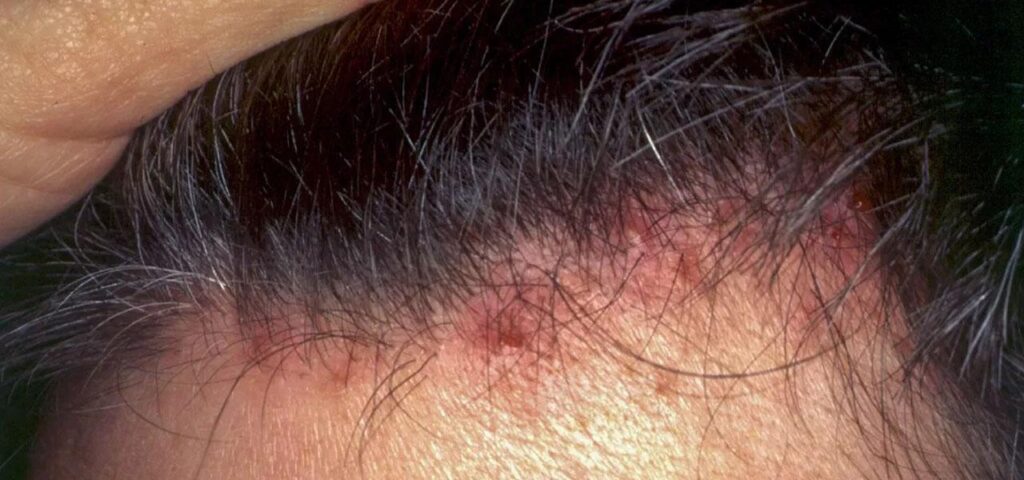
- Another reason for itchy scalp is ringworm. Depending on its type, foci of alopecia are observed, which are accompanied by desquamation of the skin surface, as well as painful inflammatory infiltrates or nodules with exuding purulent contents.
- In addition, with an itchy scalp, patients often suspect psoriasis. It manifests itself with characteristic skin lesions that result from a disturbed epidermal regeneration process. They are distinguished by a distinct border, red/brown color and flaking of epidermal sheets from the surface of the lesion.
- Another cause that causes itching of the head, is allergic contact dermatitis. They are caused by small-molecule haptens that penetrate the skin and trigger an immune system response. For eczema to appear, the patient must have some predisposition to hapten contact allergy. This can include nickel, formalin or fragrances.
What are the characteristics of dandruff?
Dandruff is a type of ringworm, the symptoms of which are caused by the fungus on the skin Malassezia. It is a lipophilic species, using lipids found in human sebum as a source of energy for growth and development. The metabolites produced during the breakdown of triglycerides irritate the epidermis, causing inflammation in it, which promotes faster exfoliation of the dead layers of the epidermis. Then there are the typical flakes and white scales on the scalp, which can be in the form of dry or oily dandruff. The disease is recurrent and is caused by genetic, external or hormonal factors. When treating dandruff, it is usually enough to introduce a home treatment with an anti-dandruff shampoo. It contains active substances with antifungal properties.
Why does seborrheic dermatitis cause itching?
It is an inflammatory condition whose symptoms involve an area with a large number of sebaceous glands – the scalp, chest or back. Similar to dandruff, Malassezia fungi, excessive sebum production and abnormal cellular reconstruction of the epidermis, leading to accelerated keratosis, are believed to play a large role in the development of the condition. Psoriasis also often occurs simultaneously with oily dandruff, being recurrent and chronic in nature.
Read more: Seborrheic dermatitis – causes, treatment of SEA
The condition occurs during puberty, when the sebaceous glands are excessively active. The next peak in incidence, on the other hand, is after 50. year of age. The lesions can be recognized by reddened skin, exfoliation of the epidermis and itching that intensifies, for example, during stress and perspiration. During treatment, too, shampoos and antifungal medications are mainly used.
What is the course of psoriasis?
It is a chronic inflammatory skin disease of autoimmune origin. The deterioration of the skin is caused by Malassezia fungi, and the condition itself is related to the improper functioning of the immune system. The normal cell cycle in the skin lasts equally 28 days. During this time, skin cells form, mature and die and naturally peel off. In psoriasis, the immune system signals much earlier to shorten the whole process to 3-4 days. So the new cells mature very quickly, and the old cells can’t keep up with exfoliation. As a result, a thick layer of dead cells in the form of scales is formed on the skin. The symptoms are red, scaly, itchy inflammatory foci on the skin, which are covered with silvery scales. When scraped off, the scales fall off in the form of thin flakes and highlight the shiny surface.
Read more: Psoriasis of the scalp – causes, symptoms, treatment
In most cases, external therapy is used during the treatment of psoriasis to remove the excessive layer of scales and inhibit the excessive production of new epidermal cells. It is also important to regularly moisturize and lubricate the scalp to prevent micro-damage to the skin.
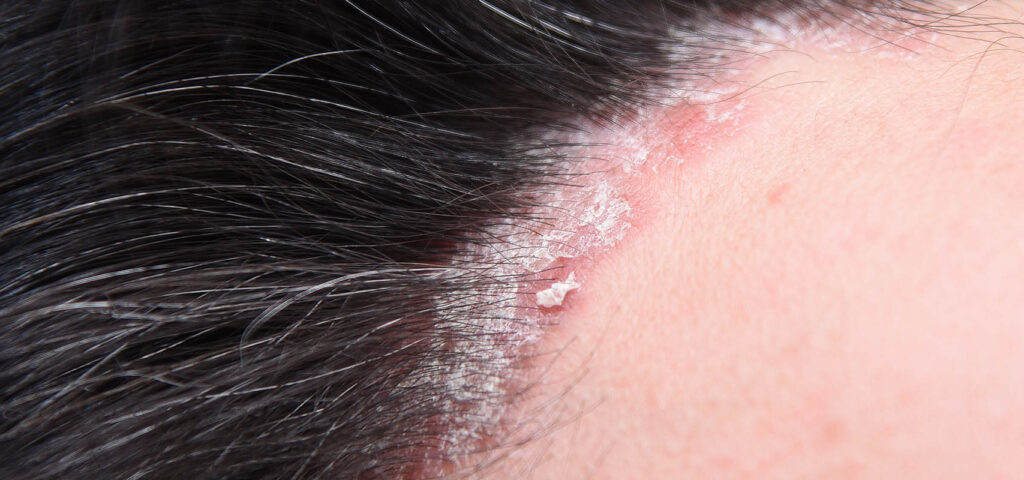
What is atopic dermatitis?
It is a chronic, recurrent inflammatory disease of the scalp of allergic origin. It progresses with increased pruritus, typical appearance of the location of skin lesions. It usually occurs in children, but also develops in adults. The disease can even last a lifetime, but in most cases the symptoms resolve by school age.
Atopy is called the hereditary tendency to overproduce immunoglobulin E and develop an immediate-type allergic reaction, which is a response to contact with a minimal amount of allergen. Malassezia fungi play a key role in the development of AD. In the course of the disease, the metabolism of epidermal lipids is disturbed, resulting in improper construction of the hydrolipid mantle. In addition, the intercellular binder that binds the epidermal cells together does not bond them tightly enough and makes the skin of AD patients like a sieve for external irritants or allergens. Skin devoid of the hydrolipidic mantle is dry, rough and itchy. Redness, small pimples and papules, and even thickened scales appear on the head.
When the condition is exacerbated, anti-inflammatory and antifungal drugs are used. Proper care and the use of shampoos with moisturizing ingredients to wash the scalp and hair also play a big role in the treatment.
Patients with AD very often fall into what is known as “the disease. a vicious cycle, as dry skin and the accompanying itching makes them scratch. This in turn leads to further damage to the epidermis and exacerbates dry skin. Allergens, irritants and microorganisms also penetrate more easily. In addition, this exacerbates local inflammation. All this further aggravates the itching.
What is scalp contact allergy?
It is an acquired hypersensitivity to a particular allergenic ingredient. It occurs when the scalp comes into contact with the agent. Then itching of the skin, eczema, redness develops. Allergenic substances commonly include, for example:
- Nickel – found in hair ornaments,
- Paraphenylenediamine – an ingredient in hair dyes,
- Propylene glycol – a solvent in cosmetic aerosols,
- Sodium lauryl sulfate – an ingredient in shampoos,
- Formalin – used for hair straightening treatments,
- Cocamidopropyl betaine – a detergent used in shampoos,
- Fragrances.
When contact allergy is suspected, the allergenic agent should be discontinued as soon as possible. Treatment uses topical medications to soothe the reaction, which are recommended by a dermatologist or trichologist.
What are the characteristics of a dry scalp?
Itching of the scalp is also a symptom of skin dryness, which occurs without obvious peeling of the epidermis
. The trouble usually stems from inadequate care, external factors, hormonal changes. The causes of excessive dryness of the scalp are also diseases involving disorders of the structure and function of the epidermis or systemic diseases. Rapid improvement of the scalp is noted with the use of dermocosmetic shampoos. Additional support for the treatment of this condition is mesotherapy in an aesthetic medicine office.
What is folliculitis?
A hair follicle is a slit in the skin from which a hair grows (check out hair structure here). Each follicle has its own sebaceous gland, which produces sebum to moisturize the scalp. At the bottom of the follicle is a papilla, and around it is a matrix composed of hair cells. These cells gradually grow and mature to pierce the skin as new hair. Unfortunately, sometimes inflammation develops within the hair follicle. This is due to bacteria residing in the skin (Streptococcus suppurativa and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria). This results in purulent papules, redness and itching. Depending on the pathogen, various antibiotics and antifungal drugs are used during treatment, which are recommended by the dermatologist.
Read more: Folliculitis – causes, symptoms, treatment
Does head lice cause itching?
It is an infectious disease caused by human lice. They inhabit the scalp, laying eggs in the hair. Lice feed on blood, and an inflammatory reaction develops at the site of the bite, accompanied by severe itching. The easiest symptom of this disease to observe, is precisely the strong scratching. Treatment is topical – shampoos or sprays with an antivaxxin active ingredient are used.
What else causes itchy scalp?
Although not everyone realizes it, vitamin deficiencies are a big factor in the development of itchy scalp. Lack of key minerals can affect the condition of hair and scalp. Pruritus is closely related to B vitamins.
Stress is also not indifferent to the condition of the scalp. Strong emotions can reverberate in the form of just itching. Numerous studies show that hormone-induced scalp itching is related to stress. Cortisol, adrenaline or norepinephrine are responsible for strong emotions, but they can also cause dry mouth and an uncontrollable need to scratch your head.
How to treat an itchy scalp?
The treatment depends on the type of disease present and the condition. External action refers to the use of appropriate shampoos or creams. If the patient has a severe form of the disease or its recurrence, then oral therapy combined with topical therapy is implemented.
An important step in therapy, is also proper hygiene of the scalp – especially frequent washing of hair with hypoallergenic shampoos. The patient should choose a shampoo for dry and sensitive skin. You can also use home remedies:
- Menthol applications with anesthetic and irritation-reducing effects,
- The use of camphor, which gives a cooling sensation,
- Cold packs of any form of frozen products,
- Infusions of plantain, which naturally relieves itching.
However, regardless of the type of condition, it is advisable to go to a dermatologist and a trichologist for advice if the first symptoms are present. A specialist, based on an evaluation of the scalp, history and examination with a dermatoscope, can make an accurate diagnosis and incorporate the appropriate treatment.
- What’s new in the etiology and therapy of seborrheic dermatitis, Aleksandra Buczek, Dominika Wcisło-Dziadecka, Katarzyna Sierant, Ligia Brzezińska-Wcisło, http://www.pnmedycznych.pl/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/pnm_2018_01A_049-054.pdf
- Pharmacotherapy of Psoriasis, Krystyna Romanska-Gocka, Department of Dermatology, Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Immunodermatology, Collegium Medicum in Bydgoszcz, UMK, Torun, %20Farmakoterapia%
- E., Jagielski T., Macura A., Bielecki J.: Characterization of fungi of the genus Malessezia. Clinical aspects. Post Microbiol 2013; 52 (3): 307-314.