A lot of people are dealing with excessive hair loss, which is not only a health problem, but also a big aesthetic issue. Healthy and thick hair is one of the attributes, that the opposite sex is most attracted to. Hair loss is a natural process for the human body. Specialists distinguish many different causes of hair loss, which can be successfully treated.
- 1. Hair loss and the phases of growth
- 2. Causes of hair loss
- 3. Hair loss forms bald patties
- 4. Receding hairline
- 5. Hair loss after pregnancy
- 6. Hair loss in women
- 7. Hair loss in men
- 8. Hair loss in children
- 9. Hair falls out because of a sick thyroid
- 10. Inappropriate hair care
- 11. Does the lifestyle affect hair loss?
- 12. Deficiency of vitamins and minerals
- 13. Hair loss treatment
- 14. Baldness in statistics
Hair loss and the phases of growth
Hair is characterized by a complex structure, consisting of stems, hair roots and the hair follicle. The bellows regulate the hair growth. It is located in the middle layer of the skin and is nourished by a richly vascularized wart. Every person has an average of 85,000 to 140 thousand hair on their body, and the development of hair follicles already starts in the utero. When the fetus is about 60 days old, the first hair follicles are starting to form on its head. Hair growth is not a continuous process, but it is characterized by 3 different phases.
During our life, these cycles are constantly being repeated, while the order of the phases stays the same. The hair growth cycle consists of 3 phases: growth, disappearance and loss. During the growth phase, the hair follicle cells intensively divide themselves to produce new hair. The duration of this phase is genetically determined and lasts from 2 to 7 years. 90% of a healthy person’s hair is in the growth phase.
The second phase concerns disappearance and lasts from 14 to 21 days. During this period, the remodelling processes occur in the hair root. The hair matrix disappears, and the hair is pushed towards the skin. For an average patient, 3% of the hair on the scalp is in this phase.
The last phase concerns completely horny hair, in which metabolic processes no longer take place. Within 30-90 days, the hair bulb becomes thinner and falls out, while brushing or washing your hair. The old hair is pushed out by the growing new hair. About 13% of a healthy patients’ hair on the scalp is in this phase.
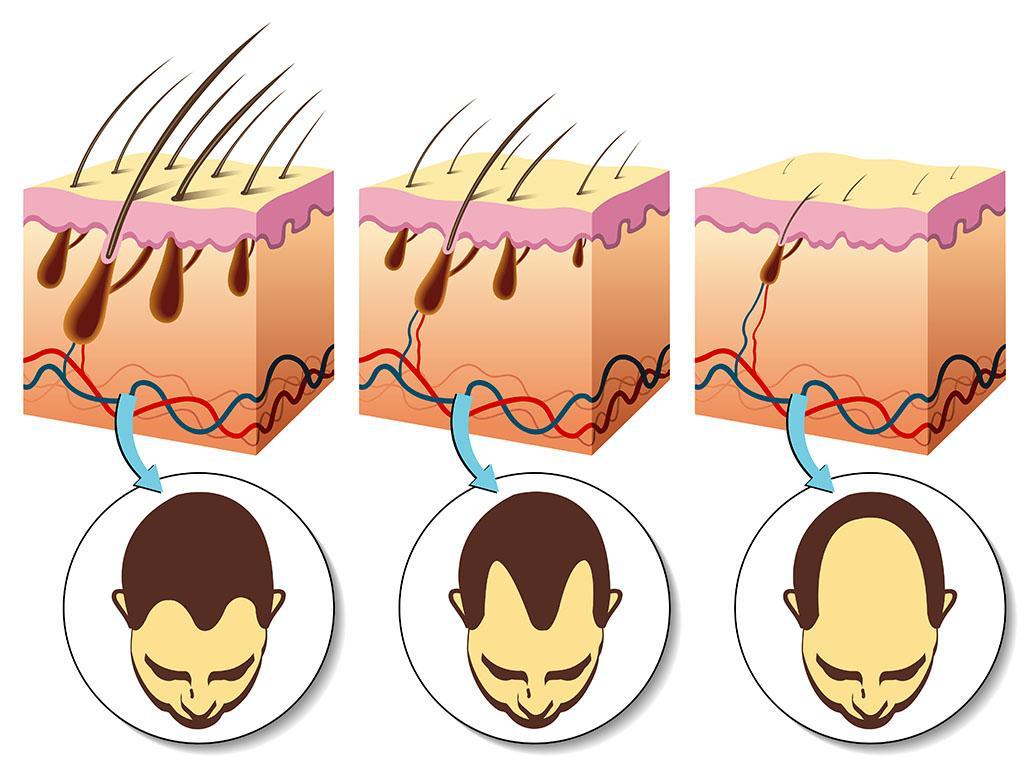
Causes of hair loss
If we notice that our hair is thinning, or we are able to see bald spots on our head or bend, then this may be a sign that you should seek advice of a pharmacist. If hair loss occurs suddenly or is extremely severe, then a consultation with a dermatologist is necessary.

The dermatologist can detect the underlying problems and pathological phenomena associated with excessive hair loss, e.g. iron deficiency, thyroid problems or hormonal problems or side effects of some medications – which can contribute to hair loss.
- Stress – during periods of increased nervousness and stress – the consequence contributes to hair loss.
- Thyroid disease – large amounts of hair loss can be a symptom of thyroid problems.
- Improper diet – hair weakness may be due to a shortage of vitamins and minerals. Such as iron, vitamin H, vitamin A, folic acid, silicon, magnesium and zinc.
- Medication – it is worth checking whether the medication we take causes side effects in the form of hair loss.
- Anemia – iron, but also zinc deficiency can cause excessive hair loss. It is worth doing blood tests regularly.
- Hormones – androgen hormone and dihydrotestosterone affect the hair follicles, causing androgenetic alopecia, occurring for men in the frontal angles (bends) or on the top of the head for women.
- Improper hair and scalp care – frequent dyeing, bleaching or the use of strong styling products does not help our hair.
- Skin diseases – ringworm, psoriasis, dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, etc.
- Seasons – due to autumn and spring solstice, our body may react to weakness and the hair might fall out more than usual. In this case, you should consider a proper diet rich in vitamins and minerals, to nourish the body and achieve the dream of beautiful and shiny hair.
Hair loss forms bald patties
Alopecia areata also affects children and can occur at any age. This disease is defined by transient or permanent periods of baldness, and the affected areas have different sizes and shapes. Alopecia areata can also affect other body parts, even the eyebrows or eyelashes. The course of the disease is very diverse, and the symptoms can affect one or several smaller outbreaks.
Hair regrowth occurs spontaneously, and the disease is distinguished by periodic exacerbations of symptoms. Symptoms of the disease are oval or round foci on the scalp, which often blend together. The main cause of this disease is inheritance. The appearance of alopecia areata is also influenced by autoimmune diseases, stress, and taking various types of medication. The cause may also be a disorder of the hair growth cycle, i.e. the hair dyes too fast.
The diagnosis of this disease is not complicated, and a visual examination of the scalp is often enough. To effectively treat alopecia areata, you need to know the cause and eliminate it. The right treatment consists of using medication in the form of ointments. The clinic is offering treatments, that will work for alopecia areata. In this case, we are talking about mesotherapy, i.e. subcutaneous administration of nutritional mixtures.
A form of therapy by using radiation or scalp massages will also be effective. The doctor will choose the right type of therapy for every patient.
Receding hairline
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common cause of hair loss. For men, the disease manifests as bends, and women are suffering of thinner hair over the entire surface of the head. The patients’ hair follicles are hypersensitive to androgens, which causes hair weakness and hair loss. As a result, the hair follicles are miniaturized, and the hair growth phase is shortened.
This means that the hair falls out much easier, and new ones appear in their place later. The causes of androgenetic alopecia not only include the influence of androgens, but also the general lifestyle. Stress, occupational factors, aggresive hair care, polycystic ovary syndrome or oral contraceptive use are some of the most common causes of this disease.
When treating androgenetic alopecia, the focus should be primarily on eliminating the causes of the disease. The treatment involves the use of medications that nourish the hair follicles. Doctors recommend performing a hair transplant using the modern FUE method, which involves transplanting individual hair follicles. To prevent this disease, a healthy lifestyle and the introduction of a diet with a low glycaemic index, is a good start.
Hair loss after pregnancy
Intensive hair loss after a pregnancy is a typical problem for young mothers, which often causes embarrassment. Hair loss after delivery is not a sign of a worse state of health, depletion of the body or loss of nutritional value. The cause of hair loss after pregnancy is an altered hormonal balance.
Thanks to a significantly increased level of oestrogen in the body during pregnancy, the hair does not fall out, but becomes stronger. It is normal to have more lushes, thicker and shinier hair during this time. However, the decrease in oestrogen and progesterone levels after delivery, causes severe hair loss, with the consequence that hair gets significantly thinner after the pregnancy.
It is estimated that up to 20-30% of hair can be lost within two or three months after pregnancy. Hair loss after pregnancy is due to the fact that both hair, ones that should fall out at the current time, as well as those falling behind during pregnancy, are falling out.
The process of thinning hair after pregnancy can last from 6 to 9 months. In case of breastfeeding, the period of hair loss after pregnancy may be prolonged, due to the high concentration of prolactin in the body and the loss of valuable minerals, which are somehow “rinsed” from the body, so that they can be found in breast milk. Stress or other negative factors may further intensify the phenomenon of excessive hair loss after pregnancy.
Hair loss in women
Excessive hair loss in women can be permanent or transient. Hair thinning can cover a selected part of the scalp or the entire surface. The causes of hair loss in women can also be very different. Many women over 30 notice the first signs of the so-called androgenetic alopecia.

It results from the increased concentration of androgens in the blood, which is a group of hormones recognized as “male hormones”. Increased levels of testosterone, which is produced in the ovaries and adrenal cortex, lead to hair loss in women. Any significant decreases in progesterone and oestrogen levels, or a significant increase in prolactin levels, also intensify hair thinning in women, and this type of hormonal surge occurs especially in the postpartum and breastfeeding period.
Another reason for women’s hair loss is also subjecting them to destructive hair styling treatments, such as straightening or dyeing. Intense hair styles or strong combing in the so-called ponytail, can also lead to damaged hair follicles and increased hair loss.
Hair loss in women can also occur as a result of many skin diseases (e.g. lichen planus, mycosis) and systemic diseases, especially those with a hormonal background (e.g. hypothyroidism). Stress or the adverse effects of medications, including contraceptives, are also significant.
Hair loss in men
In most cases, hair loss in men is genetic. Men are bearers of the so-called alopecia gene, which is usually inherited from the father. Genetic alopecia in men accounts for 2/3 of hair loss cases. This baldness usually begins around the age of 40, covering the temporo-frontal region at the beginning and causing bends. In the later phase, hair thinning travels to the forehead and at to the top of the head.

The amount of hair around the perimeter usually decreases slightly. Genetic alopecia in men, in a very severe form, can start at the age of 16-18 and show rapid progress. It is estimated that male pattern baldness (so-called androgenetic alopecia) affects up to 60% of men aged 50 and up.
Hair loss in men is mainly associated with the action of the derivative of the male sex hormone – testosterone. This derivative called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), affects the hair follicles, making the hair thinner and weaker, and the growth phase is shortened.
Under its influence, the process of hair regrowth is also inhibited, therefore in places where the hair gets lost, no new ones are formed. All these factors eventually lead to hair loss in men, which results in significantly thinner hair or a complete alopecia.
Hair loss in children
It is estimated that hair loss in children is a problem that causes about 3% of children’s medical visits. It can often have very diverse and complex causes. If we take a look at an infant’s hair loss, there is no reason to worry. We need to know that this is a natural physiological process – a few or even a dozen or so weeks after birth, the child somehow “changes hair”.
However, the lost hair is quickly replaced by new ones. The cause of hair loss in children in infancy can also be ordinary rubbing of the head against the car seat or sleeping for a long time in the same position. A result of pressure on the scalp and the delicate structure of the child’s hair. Hair thinning in a child may also be due to a disease (e.g. syphilis infection, fungal infection, thyroid disease, diabetes). The child’s fragile immune system can attack the hair follicles, leading to a so-called Alopecia areata, which in addition to hair loss on the scalp can also lead to eyelashes, eyebrows or pubic hair loss.
The causes of hair loss in slightly older children, may be related to psychological problems. Stress, a difficult family situation, excessive demands from parents or frequent quarrels at home, certainly do affect the child’s psyche, and thus the condition of his hair. This can lead to telogen baldness, which causes the hair to go into a rest phase first, and then falls out excessively.
Thinning hair in a child is also a frequent result of nutritional neglect. It is also worth remembering to avoid over-stretching the child’s hair, e.g. when braiding a braid or tying a ponytail.
Hair falls out because of a sick thyroid
Correct thyroid hormone levels affect the condition of your hair and the proper functioning of your entire body. Specialists distinguish two types of thyroid dysfunction: hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Patients with hypothyroidism suffer from rough, dry hair and it falls out very easily.
The disease is also accompanied by fatigue, weight gain, muscle weakness and skin changes. Deficiency of thyroid hormones affect the metabolic changes in the body’s cells in a negative way. In the hair cells, the amount of transformation also decreases, and more hair goes to rest. Hair then falls out faster, and the condition of the hair is also heavily affected by the swelling of subcutaneous tissue. Hair loss stops if the hypothyroidism is treated effectively.
The second common thyroid disorder is hyperthyroidism, which is the excessive production of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Patients have excessive weight loss, hyperactivity, arrhythmias and increased sweating. The patients’ hair is very thin, and it is distinguished by excessive gloss. Excess thyroid hormones accelerate the transition to the dying phase, which results in excessive hair loss. Equalizing hormone levels means reducing hair loss and their gradual regrowth.
Inappropriate hair care
Inadequate daily care can contribute to weakness and hair loss. Using strong cosmetics for washing or styling (hair gels, varnishes) significantly weakens the condition of the hair and can lead to brittleness and weakness of the hair follicles. In weakened skin, there is a circulatory disorder, which significantly affects the nutrition of the hair follicles.
Daily use of a hair dryer or straightener will also be a problem as it will dry and break your hair. Hot temperature also affects the condition of the scalp and weakens the hair follicles, which are responsible for hair growth. Common mistakes also include a strong hair tie or hairpin that pulls the hair tight. Such hair styles also weaken the hair follicles and will lead to deterioration of hair quality and excessive hair loss. Using the wrong brush or comb also leads to hair loss.
In women, dyeing is a common cause of hair loss. Strong chemicals contained in the hair dye lead to weakening of the hair and hair loss.
Does the lifestyle affect hair loss?
Many patients, struggling with the problem of excessive hair loss, are affected by an inappropriate lifestyle. One of the most common mistakes is an unhealthy diet rich in sugar and highly processed products. The diet plays a particularly important role in building a strong hair condition.
A healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals will allow you to provide your body with all the necessary ingredients. Correct circulation in the scalp means good nutrition of the hair follicles, which will stimulate hair to grow. Specialists especially recommend a diet with a low glycaemic index, that will help prevent the development of diabetes. Stress, which weakens all body processes, also has a great impact on baldness.
It was also noticed that patients who smoke cigarettes have a worse condition. They are then more dull, dry and prone to breaking and falling out. The lifestyle should also include the right amount of sleep and rest, which will enable the regeneration of the body and the correct course of many processes occurring in it.
Excessive exposure of the hair and scalp to sunlight and solarium will also weaken the condition of the hair.
Deficiency of vitamins and minerals
The right amount of vitamins and nutrients can stop excessive hair loss and keep them fit. It is worth mentioning, that an incorrect diet, low in nutrients, will quickly affect the condition of the hair and will lead to its weakening. Excessive hair loss may be the result of a vitamin A deficiency, which plays an important role in the proper keratinization of hair cells.
The lack of vitamin A makes the hair dry and brittle. Vitamin E also plays an important role, which promotes scalp circulation and protects the hair against harmful effects of free radicals. Vitamin D also plays an important role, because it is able to activate hair growth and stop the genes responsible for baldness. The action of vitamin D will be supported by vitamin C, which stimulates hair regrowth and protects from hair loss. Vitamin H, also called biotin, not only prevents hair loss but also baldness.
Biotin contains a lot of sulphur, which is necessary for maintaining healthy and strong hair. It will also prevent dandruff and seborrhoea of the skin, which significantly weakens the condition of the hair. Vitamin PP, or niacin, facilitates the transport of nutrients to the hair bulb. B group vitamins, which stimulate new hair growth and stops hair loss, are also very important.
Hair loss treatment
A conscious daily hair care, using natural cosmetics, plays a very important role. Good compositions of shampoos and hair conditioners will strengthen the hair and will nourish the scalp. The correct lifestyle is also important, i.e. the right amount of sleep, avoiding stress as well as quitting smoking.
A healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals will also play a large role in maintaining the health of the whole body and a good hair condition. Specialists emphasize to avoid sugar and chemical additives in the diet that contributes to the disruption of various processes in the body. By preventing hair loss, we also understand the use of proper vitamin and supplementation of nutrients.
Undergoing examinations regularly, will detect various types of disorders that play a huge role. An early treatment will allow you to get the desired results and quickly get rid of the problem of excessive hair loss. Awareness of patients and, if necessary, a quick visit to a specialist is very important in the prevention of scalp diseases.
Baldness in statistics
When we are in good health – daily hair loss can be from 50 to 70 or even 150 pieces. The number of hair loss above this upper limit should alarm us and determine us to see a specialist for a proper diagnosis.
The average person has about 100,000 hair. Each hair follicle produces hair that grows from a few to several millimetres in a month. The hair growth phase lasts on average from two to six years. Just before falling out, the hair is at rest. It is quickly replaced by new hair and the cycle starts again. At least 85% of the hair on the head should be in the growth phase. Hair in the resting phase falls out systematically. It is a natural and physiological process. Most people see about 50-100 hairs falling out per day.