Selenium is a chemical element that is extremely necessary for the proper functioning of the body. Despite the fact, that it is enough in small amounts, it is a very important micronutrient that should not be forgotten. Both the excess of selenium and its deficiency can adversely affect the body. Too much selenium intake can cause skin inflammation, liver damage and cirrhosis, unpleasant symptoms from the digestive system, deterioration of the appearance of the nails, as well as graying and hair loss. On the other hand, the deficiency of this element results in the imbalance of the immune system, depression, the possibility of miscarriages or premature births, increases the risk of e.g. multiple sclerosis and Hashimoto. In addition, selenium deficiency can damage the work of our heart, accelerate aging, increase susceptibility to diseases and cause hypothyroidism.
The influence of selenium on the proper functioning of the human body
A proper selenium supply significantly improves the condition of the body. When the right doses are taken, this micronutrient helps to strengthen the immune system, which will start to deal more efficiently with the viruses, bacteria, herpes and shingles that attack it.
Even more, regular consumption of products containing selenium (or its proper supplementation) reduces the risk of diseases in the body, such as prostate cancer, cancer of the anus, lung and cervix, due to the action of neutralizing free radicals. This action also improves the condition of the skin and hair, as it prevents premature aging of cells.
The effects of selenium deficiency and its effect on hair
A selenium deficiency in the body, can often have symptoms similar to iodine deficiency. There is also a high risk of developing goiter, as well as the appearance of symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Bad selenium supplementation is directly visible on the hair. Its deficiency can cause a problem with greasy hair and dandruff, and the excess of the element results ingraying and hair loss. A proper supply of selenium guarantees the elasticity and bounce of the hair, and prevents excessive hair loss. It is also very helpful in obtaining lush, healthy hair, and thanks to its antifungal and antibacterial properties, it helps to protect it. against scalp inflammation.
What products contain selenium?
This element can be found in in yeast, but first pour boiling water over it before consuming. Only 2g of brewer’s yeast a day is enough to cover the body’s needs of selenium. Other foods rich in this micronutrient also include nuts, seeds, liver, seafood, fish, sprouts, vegetables – especially those grown in selenium-containing soils. Large amounts of this element can also be found in products such as garlic, lentils, white beans, tuna, cod, sesame seeds, barley groats, cabbage, lettuce, flax seeds, mustard and chicory root.
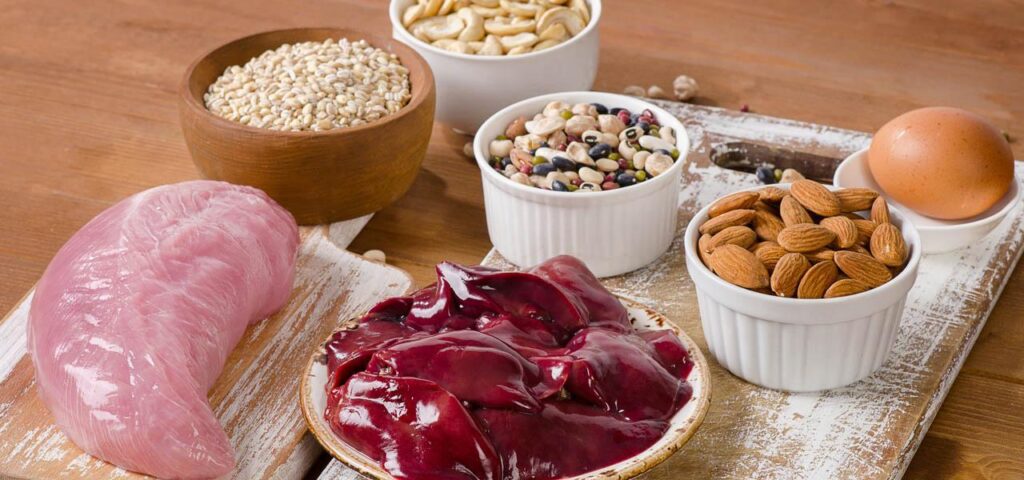

If you want to ensure the proper supply of selenium, it is also worth enriching your diet with:
- Noble boletus – these mushrooms contain as much as 3600 micrograms of selenium per 100g of dried product.
- Brazil nuts – are a valuable source of good selenium, one brazil nut contains 103 to 219 micrograms of this chemical element. In addition, these nuts are also an excellent example of a product that provides the body with unsaturated fatty acids, which reduce bad cholesterol.
- Salmon– fresh salmon provides as much as 32 micrograms of selenium, and in 100g of smoked fish – about 26 micrograms. In addition to the fact, that these fish are already very healthy, they also provide many unsaturated fatty acids and a large dose of nutrients.
- Sunflower seeds – 100 g of seeds contain as much as 70 micrograms of this microelement. In addition, sunflower provides the body with vitamins E and B.
- Eggs – 100 g of eggs provides about 23 micrograms of selenium. This product also does not contain vitamin C, which adversely affects the absorption of selenium by the body.
Daily requirement for selenium intake
The daily selenium intake recommended by specialists is around 45 micrograms a day. The exception, however, are pregnant women and breast feeding mothers, who should consume 400 and 360 micrograms of selenium daily (due to the low level of this element in the mother’s body, the risk of developing asthma in the child may be increased).
In case of a deficiency of this chemical element, it is very important to make up for its deficit at the beginning. That is why it is recommended to start with a daily dose of around 100-200 micrograms per day.
Selenium supplementation (other than that available in food products) should be consulted with a doctor so you will not expose yourself to an unnecessary risk of an excess of this element in the body.