Minoxidil is a popular drug that is used to treat androgenetic alopecia, as well as excessive hair loss or weakening for other reasons. It yields satisfactory results, and its inclusion in therapy has a relatively low risk of side effects. Find out everything you need to know about minoxidil.
- 1. History of minoxidil
- 2. What is minoxidil?
- 3. When is minoxidil therapy recommended?
- 4. Minoxidil – application
- 5. Can minoxidil be used on the beard?
- 6. Feedback and safety
- 7. Minoxidil – effects of use
- 8. Minoxidil – side effects
- 9. Is minoxidil worth using?
- 10. Minoxidil, and finasteride
- 11. Genetics and baldness, and the choice of treatment
- 12. Is it possible to cure androgenetic alopecia?
History of minoxidil
Minoxidil was introduced to the market in 1979, when its use in blood pressure disorders began. Initially, accelerated hair growth and increased hair density were considered an undesirable effect, but over time the substance’s potential for treating baldness was recognized. Minoxidil was not registered as a drug for ailments of this nature until 1988. We use it successfully to this day, enjoying the satisfactory results of therapy with this substance.
What is minoxidil?
Minoxidil is a drug available as a solution to be applied to the scalp. Sometimes you can also find it in the form of a shampoo, foam or spray. Minoxidil tablets are very rarely used due to the side effects that can occur. It is used when the patient is facing excessive hair loss, hair weakening, hair thinning, as well as after hair restoration procedures in order to accelerate hair regrowth. It is used in both men and women.
When is minoxidil therapy recommended?
Minoxidil is applied directly to the skin, usually on the head. It is not recommended to incorporate it into therapy in people diagnosed with scarring alopecia or alopecia areata. It should not be applied to altered skin or if hair loss is progressing due to seasonal loss, pregnancy or thyroid disease. Consequently, it is also often not applicable to seborrheic alopecia, in the course of which we have to deal with yellow scales on the scalp, exudates, redness and irritation. Minoxidil is also not applicable in sudden hair loss without a known cause – in such situations, the cause should be sought and eliminated.
Although minoxidil in lower concentrations is available without a prescription, it should not be applied to the skin without first consulting a specialist. The agent should be used only on the clear recommendation of a doctor and after positive qualification of the scalp for therapy with this substance. Minoxidil is sold as a 2% and 5% solution.
Minoxidil – application
Apply 1 ml of the solution to the scalp affected by baldness and spread with fingertips. Then wash your hands. The procedure is repeated twice a day. The effects of the therapy are usually noticeable after a few months. To make it easier for patients to use the drug, you usually get two different dispenser tips along with it – a nozzle and an applicator.
The former makes it easy to measure out the right amount of the drug, while the latter allows it to be accurately applied to the hairy area affected by excessive hair loss. A 5% solution is most often recommended for men, while a 2% concentration is recommended for women. Minoxidil should be applied to the skin no later than 2 hours before going to bed.
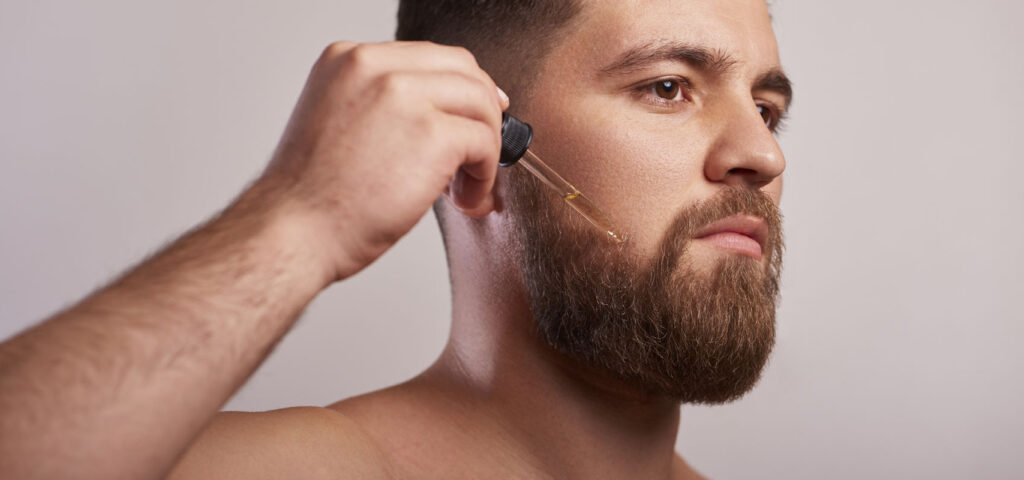
Can minoxidil be used on the beard?
As a general rule, minoxidil is used on the top of the head, and that’s where it gives better results than on the bends. Can it also be used on the beard? Yes, but only under the supervision of a doctor. It will prolong the hair growth phase and make the beard look as if it is much thicker. However, you need to keep in mind that the skin in these areas is delicate and, in addition, often irritated by razors, so you need to be extra careful. Nonetheless, minoxidil is one of the quite popular preparations used by bearded men.

Feedback and safety
Minoxidil is effective in about 60% of patients who opt for therapy with it. Reviews of its use are rather positive, and side effects rarely appear, provided the product is applied and dosed according to the instructions on the leaflet or those formulated by the doctor. It is a well-researched drug that has been used to treat baldness for years. It has not been found to have any negative effects on the body, and what’s more, 95% of its metabolites disappear after just a few days of treatment.
However, it must not be used during pregnancy and lactation, as it is not known what effect it may have on the fetus. Studies have been conducted on this subject in animals, where minoxidil showed negative effects on their fetuses, but no such data are available on humans. The effects from the use of minoxidil are widely considered to be very satisfactory, due to the relatively fast duration of action and the visibility of the results to the naked eye.
Minoxidil – effects of use
The first effects of minoxidil usually appear after about 4 months. Initially, the hairs grow back thin and fine, but over time they become as tough as the others. Sometimes it happens that after a few weeks of use, patients notice increased hair loss – but this should not be worried, as it is related to the effects of the drug.
What are the effects of minoxidil?
- It causes better blood circulation to the scalp and nourishes the hair follicles,
- Makes hair grow faster and make it thicker and stronger,
- Prevents the accumulation of exfoliated epidermis at the mouths of the sebaceous glands, and consequently reduces the risk of imperfections or inflammation on the scalp,
- prolongs the hair growth phase and delays its entry into the telogen phase, so more hair stays with its owner for longer.
How does minoxidil not work? It certainly does not have an anti-androgenic effect, so it will not completely get rid of the problem of androgenetic alopecia. The greatest results can be observed after a year of minoxidil use, and the most susceptible group to its use are young men. Although detailed studies on this topic are lacking, the medical community reports that minoxidil significantly improves outcomes after hair transplants.
Minoxidil – side effects
The drug may cause local skin irritation and dryness and aggravate orthostatic hypotension. Because it dilates peripheral vessels, it should not be combined with other preparations with a similar pattern of action. Do not take more than the recommended dose of the drug, as this can lead to tachycardia, water retention or hypotension. In addition, headaches, shortness of breath, itching and burning of the skin, inflammation, peripheral edema or skin peeling may occur.
If you experience a severe allergic reaction that manifests itself as difficulty breathing or swallowing, as well as visible swelling in the facial area, contact your doctor immediately and take the medication used or the leaflet with you. In general, however, minoxidil is very well tolerated, which is why it has become one of the most popular preparations used in the treatment of alopecia. It is also worth knowing that minoxidil itself is usually not responsible for drying, irritating the skin and increasing its reactivity, but the alcohol in which it is dissolved.
Is minoxidil worth using?
Minoxidil is a readily used product, precisely because of the results and the high level of safety of its inclusion in therapy. Both patients and doctors are fond of it. It can be used at home, applied topically, as well as in cosmetology offices, after using a dermaroller. Although the application of the product requires patients to be thorough, disciplined and patient, it is definitely worth a try if you are struggling with excessive hair loss. Only in extreme cases, in which hair loss is large and uncontrolled, although it brings results, unfortunately it does not meet the expectations of patients.
Minoxidil, and finasteride
Minoxidil is a slightly less invasive drug than finasteride, which has the effect of blocking the conversion of testosterone, into its derivative responsible for androgenic hair loss. Although its effect is stronger, it does not mean that we should start therapy with it. Finasteride is believed to be effective in reducing hair loss in more than 80% of individuals, while causing new hair growth in more than 60% of patients. As with minoxidil, its effectiveness is higher around the top of the head. The use of finasteride is recommended only for men.
Genetics and baldness, and the choice of treatment
In situations where minoxidil therapy does not have the desired effect, one may be inclined to use other hair loss preparations or perform a hair transplant. Unfortunately, androgenetic alopecia is a condition that is associated with hypersensitivity of hair follicles to DMT, a derivative of testosterone. Its occurrence may be related to genetics, as well as the immune system. Since the product does not have an anti-androgenic effect, it will temporarily stop hair loss, but it will not change its sensitivity to DMT permanently. It is likely that once you stop using it, your hairstyle will return to its previous form.
On the other hand, using anti-androgen drugs that reduce the concentration of DMT in the body can be expected to reduce hair loss (as with minoxidil), but it can also cause impotence, breast enlargement, reduced libido and ejaculatory dysfunction. Drugs with DMT-inhibiting effects permeate the blood and milk of mothers, so they cannot be prescribed to pregnant and lactating women.
Is it possible to cure androgenetic alopecia?
The use of minoxidil or alternatively other hair loss medications is not intended to cure the disease completely, as this is impossible. However, the right treatment can make it easier to keep the hair you have and inhibit the loss of more hair. It also allows for ad hoc thickening of the hairstyle. Ideally, treatment should be started at a young age and after the first symptoms of the condition are observed. In cases where hair loss is severe and the patient wants to find a method to permanently deal with the problem, a hair transplant is recommended.