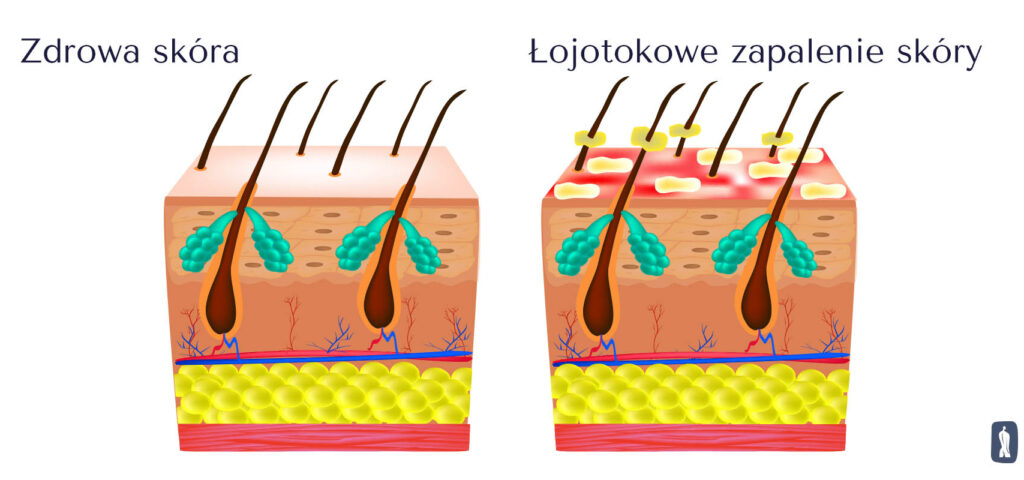
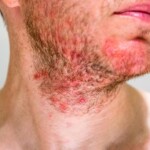
Seborrheic dermatitis affects up to 3% of the general population, more often men than women. A percentage of these people additionally develop seborrheic alopecia, which not infrequently becomes a cause of discomfort and complexes. Initially, only the condition of the scalp is deteriorated, while over time the condition includes hair loss – especially if appropriate therapeutic measures are not taken. Learn about the causes, symptoms and treatment of seborrheic alopecia.
Symptoms of seborrheic alopecia
The primary symptom of seborrheic alopecia is, of course, excessive and uncontrolled hair loss co-occurring with seborrhea, or the secretion of too much sebum, which weighs down and weakens the hair. A large number of patients complain of itching, discomfort, foul smelling skin and coverage with yellow scales. The scalp is irritated, reddened, sometimes pimples, inflammatory foci and exudates appear.
Initially, the lesions are red, dry patches. With the passage of time, they are covered with yellow scales. This is followed by severe itching, exudates, excessive oiliness and hair loss. The outbreaks are spreading and covering more and more of the head.
Seborrheic alopecia – causes of the condition
The primary causes of seborrheic alopecia include seborrheic dermatitis. A lot of stress, improper diet and health habits, unregulated autoimmune diseases, the use of certain medications, and problems with the body’s hormonal balance also don’t help. The condition occurs in both men and women and progresses in the same way in both sexes.
Although the symptoms of the disease are largely responsible for the increased hair loss, often the problem is further exacerbated by scratching the scalp and by patients scraping off the scales. This is the cause of the formation of superinfections or uncontrolled growth of Malassezia fungal populations. These are the basophytes that naturally occur in the composition of the bacterial flora found on the surface of human skin. When the immune system is weakened, their population grows excessively and becomes pathogenic to the skin. An increased population of fungi from this group is observed not only in the course of seborrheic dermatitis, but also in the course of scabby dandruff. Scratching inflammatory foci can cause the area to expand, so increased hygiene and caution is then recommended.
Seborrheic dermatitis versus seborrheic alopecia
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is not curable – it is a chronic and recurrent disease that can be silenced. Discontinuing the treatment even after the symptoms are eliminated is not advisable, because then the symptoms will probably return quite quickly. Developing appropriate habits and care regimens with the patient to keep the disease in check is key. If appropriate management is implemented already at this stage and inflammation can be reduced, perhaps increased hair loss will not occur.
Seborrheic alopecia, unlike seborrheic dermatitis, can be curbed and even cured. Moreover, it offers much more hope for getting rid of the problem than scarring or alopecia areata. In most cases, after a certain period of application of the therapy selected by the trichologist, the process of hair loss manages to stop.
After the following months, the hair follicles return to stable work, and the hair, although growing a little weaker at first, eventually returns to full strength. However, it happens that intervention is taken too late and irreversible damage to the hair follicles has already occurred. Then the only chance for the patient to regain hair is to calm the inflammatory processes on the skin and perform a hair transplant.
How does seborrheic alopecia progress?
Among the symptoms of the condition that appear first are wet dandruff and excessive scalp oiliness. Due to the scales covering it, patients’ heads begin to itch. What follows is a weakening of the hair, and eventually hair loss. In the case of seborrheic alopecia, the loss of strands begins at the temples and progresses toward the top of the head. As time passes, more and more hair falls out, so it is worth intervening at the first symptoms. A characteristic feature of seborrheic alopecia is that in the occipital area the hair usually does not fall out.
Treatment of seborrheic alopecia
The basis of the treatment of seborrheic alopecia is to look for the causes that most strongly exacerbate the symptoms of the disease. Sometimes it happens that regulating the body’s hormonal balance allows you to get rid of troublesome symptoms for the most part. In addition, medications for seborrheic dermatitis are used. Among them may be antifungal and anti-inflammatory, anti-itch and exfoliating preparations. Supportive vitamins and phototherapy are used to relieve stubborn lesions.
Properly selected care and treatments by a trichologist are also used. Their main goal is to rebuild the natural hydrolipidic barrier and find cosmetics that, in a particular case, will not cause itching, scale build-up and oily skin, while moisturizing the scalp. The key is to clean it regularly – satisfactory results are provided, for example, by trichological peels.
How do you choose care in seborrheic alopecia?
Emollients and intensive lubricants must not be used on seborrheic lesions, which will exacerbate symptoms. We are looking for gently moisturizing and soothing agents that, at the same time, do not adversely affect oily skin. The most important thing is to find the right cleansing products. These should be gentle enough not to damage the hydrolipidic layer and not give the skin a signal that additional lubrication is needed with sebum.
A dermatologist or trichologist recommends using products with the supplement:
- Ketoconazole – used in the course of Psoriasis and dandruff of unexplained etiology. It has antifungal activity. Inhibits the growth of fungi on the skin. Sometimes it dries out the hair, so it is usually applied twice a week for up to 4 weeks. After a case-by-case analysis, the doctor may recommend a different regimen of use.
- clotrimazolum – found in liquid rather than shampoo form. This is another popular antifungal agent. It provides relief from itching very quickly. It is sold without a prescription and is intended for use 2-3 times a day.
- Cyclopiroxolamine – with anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antibacterial activity. It also destroys fungal spores. It penetrates the hair follicles and skin. It deals well with Malassezia fungi and more. The list of potential side effects with the use of this agent is quite short, which is an incredible advantage.
Most often, the above-mentioned substances are contained in shampoos, but we can also find them on the market in preparations in the form of foams, gels for applying to the skin, ointments, creams and even sprays. If topically applied preparations have a bad effect on the hair, in some cases they can be replaced by tablets with the same active substance. In addition, agents containing zinc or sulfur are popular.
In the course of both seborrheic dermatitis and seborrheic alopecia, symptoms are aggravated by high humidity, so sleeping with wet hair is prohibited. If the patient participates in sports or other activities in which he or she sweats a lot, it is recommended to wash the hair immediately after exercise. Otherwise, the itching and other complaints will worsen within a few hours or the next day. In addition, an increased sanitary regime should be maintained – regular cleaning of combs and brushes, frequent changing of towels and thorough drying of hair is recommended.
What are the recommended treatments for seborrheic alopecia?
Treatments targeting seborrheic alopecia are a good idea if you are struggling with seborrhea – this can involve applying skin ampoules with individually selected active substances. Also quite popular are activities such as:
- Oxygen infusion – deals well with seborrhea, as it regulates the sebaceous glands. It reduces inflammation and is great for combating hair loss. Since high-pressure oxygen is injected into the skin during the procedure, there is no possibility of an allergic reaction. This is a suitable treatment even for irritated scalp.
- Needle mesotherapy – effective in the treatment of baldness. It involves applying revitalizing preparations to the scalp using injections. It nourishes and stimulates hair follicles. Micro-needle and needleless mesotherapy can also be performed on the scalp. Remedies containing minoxidil and biotin work well for the problems in question.
- Carboxytherapy – improves microcirculation, reduces oily hair and inhibits hair loss. It is recommended both prophylactically and therapeutically in seborrheic alopecia. It can be used simultaneously with mesotherapy and platelet-rich plasma treatments. It also deals relatively well with other types of alopecia and psoriasis.
- Botox for hair – injected into the scalp, it inhibits the activity of sebaceous glands. It reduces sweat secretion, so it can alleviate symptoms associated with post-workout aggravation. It is readily chosen by doctors and patients, well tolerated by them and recommended.
An excellent choice in the course of the condition will be to regularly perform a trichological or cavitation peel, depending on what the specialist recommends during the consultation. These will help inhibit seborrhea, safely get rid of scales and lingering dead skin, and allow deep cleansing of the skin. As a result, it will be prepared for the application of therapeutic active substances.